EML File
Phishing mail analysis
Summary
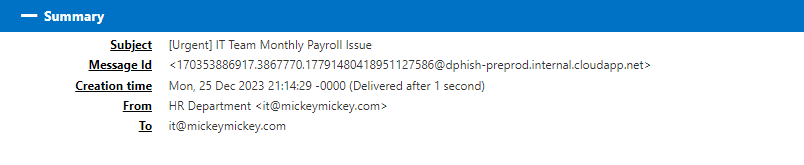 summary The email pretends to be from a legitimate source and includes an attachment that, at first glance, appears to be a harmless file (in this case, disguised as a
summary The email pretends to be from a legitimate source and includes an attachment that, at first glance, appears to be a harmless file (in this case, disguised as a .wav file). However, upon closer inspection, it is clear that the attachment is actually an .html file containing hidden scripts that can execute malicious code once opened in a browser.
Technical analysis
1-legitimate traffic:
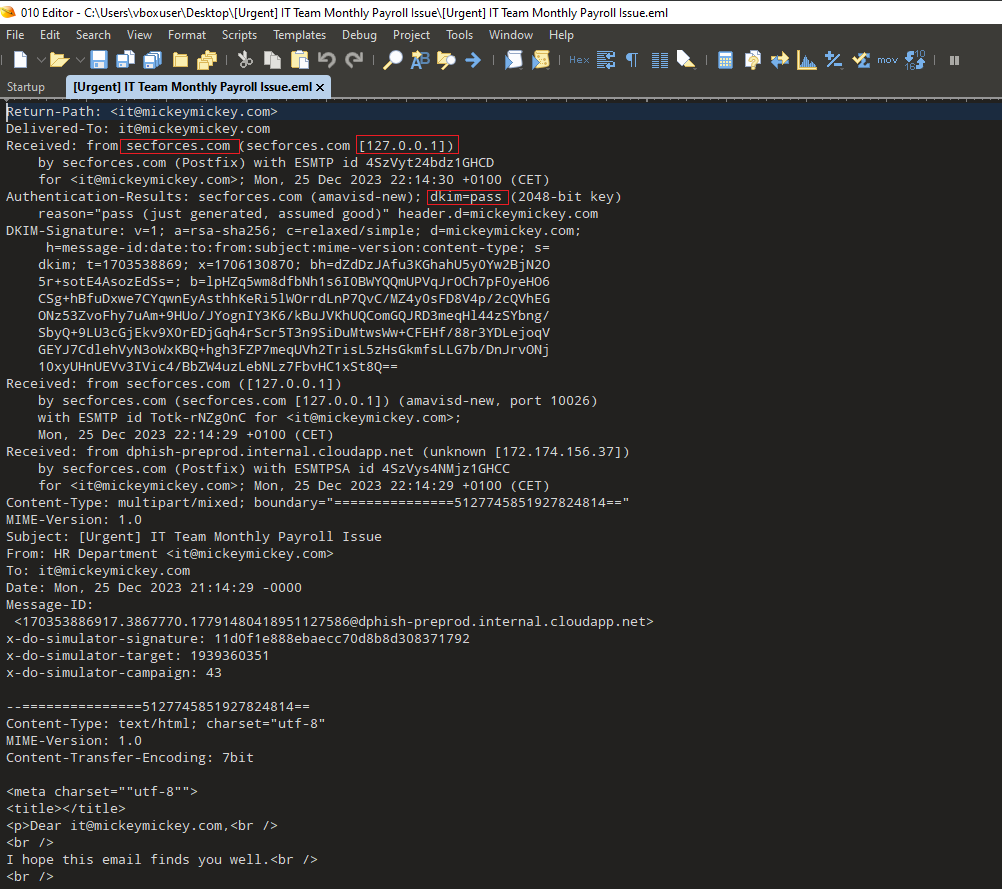 mail header attackers often take advantage of legitimate email processing systems to make their phishing attempts seem more authentic. For instance, when they use the loopback address
mail header attackers often take advantage of legitimate email processing systems to make their phishing attempts seem more authentic. For instance, when they use the loopback address 127.0.0.1, it can make it look like the email is coming from within the organization itself. Plus, by employing DKIM signatures, they can further legitimize their emails. This clever tactic can really help them slip past security controls, especially if the system isn’t properly configured. It makes detecting these phishing emails much more challenging.
2-Mail Connection:
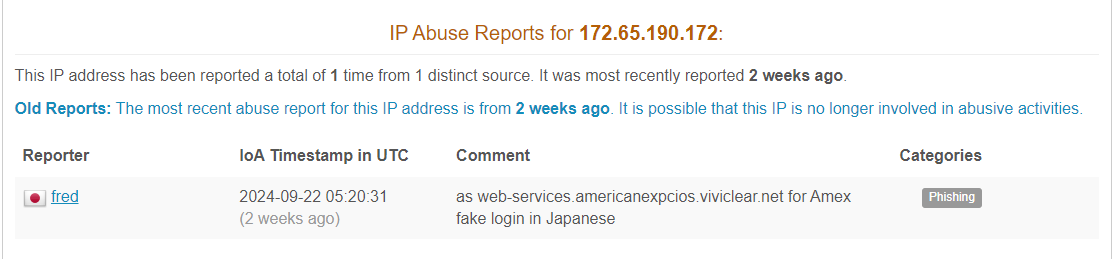 abuseipdb report details from
abuseipdb report details from AbuseIPDB:The analysis of http://secforces.com/ involved a fake login page for American Express, indicating the intent was to harvest user credentials.
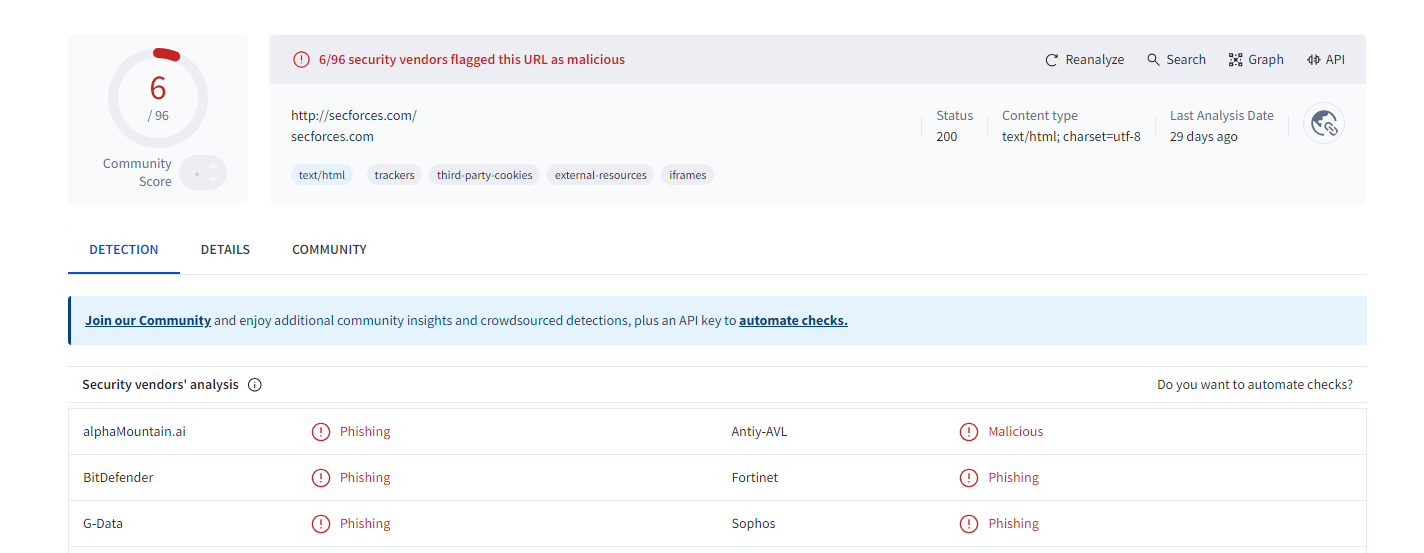 virusTotal report details from
virusTotal report details from virusTotal: The analysis of http://secforces.com/ indicates that it is associated with malicious activity, particularly phishing.
3-Malicious Attachment
 obfuscate The file is named with a
obfuscate The file is named with a .wav.html extension, which is designed to confuse the recipient into thinking it’s an audio file, but it’s actually an HTML file. This is a common trick used to bypass email security filters by disguising the file type.
4-Payload
 payload The attached
payload The attached .html file contains obfuscated JavaScript within HTML tags. This script is designed to run automatically when the file is opened.
how to detect??
- Mail Gateway Security
- Endpoint Protection
- Threat Intelligence Integration
- Implement Advanced Email Filtering
- Implement a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Monitor for Indicators of Compromise (IoCs).
By employing a combination of technical controls, user education, and proactive threat monitoring
References
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1598/002/
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/email-security/dmarc-dkim-spf/
- https://www.mimecast.com/content/dkim/

